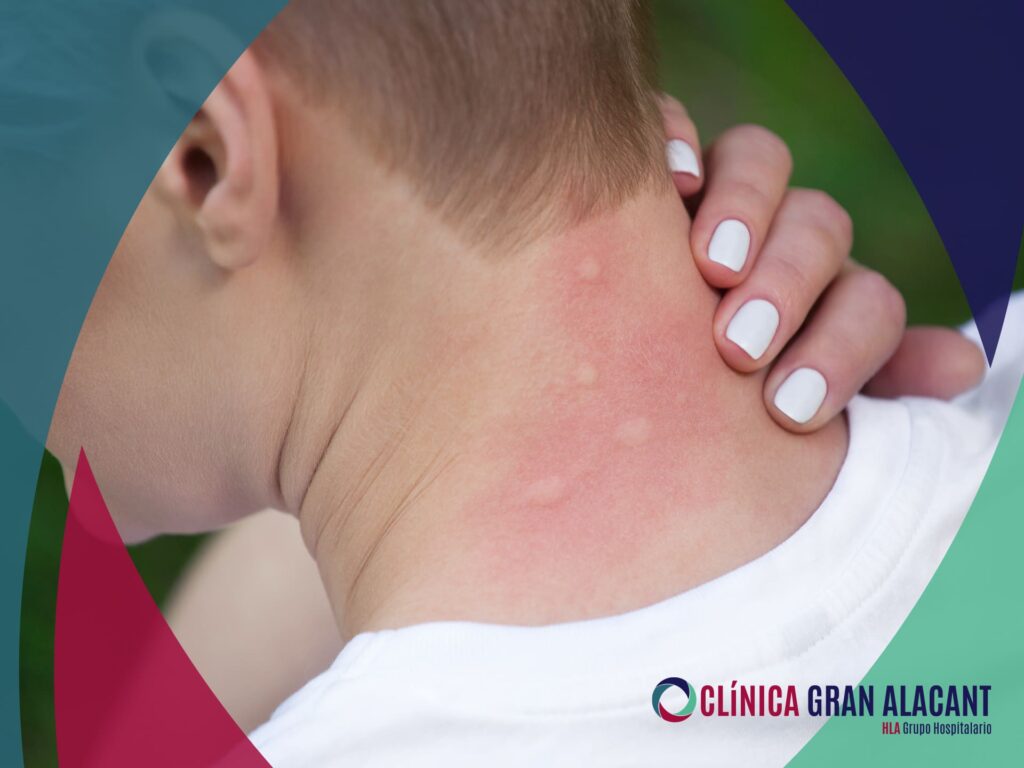
In this post we are going to talk about various types of insect bites, with pictures of them, so that you can recognise them.
Experiencing an insect bite can be a bit unsettling, especially if you don’t know what little creature left you with a red, throbbing bump on your skin. However, there is no need to panic. Most common insect bites are harmless and heal quickly. However, some stings, such as those of fire ants, wasps, hornets and bees, can cause severe pain or even a severe allergic reaction. Others, such as bites from poisonous spiders, require emergency medical attention.
Symptoms of insect bites
Symptoms of insect stings provide information about the cause and severity. For example, most stings cause redness with pain, itching or burning. Some may blister or swell. Here are some common signs related to insect bites:
- Bedbug bites leave a small, red, itchy mark on the skin, which in rare cases causes a serious allergic reaction.
- Bee stings cause a reddened elevation on the skin with a white halo around it.
- Flea bites cause an itchy bump on the skin, often on the ankles and legs.
- Mosquito bites produce a pink elevation on the skin that itches or, in rare cases, triggers a severe allergic reaction.
- Spider bites can manifest with mild symptoms such as redness, swelling and pain in the area, or more severe symptoms that require emergency care.
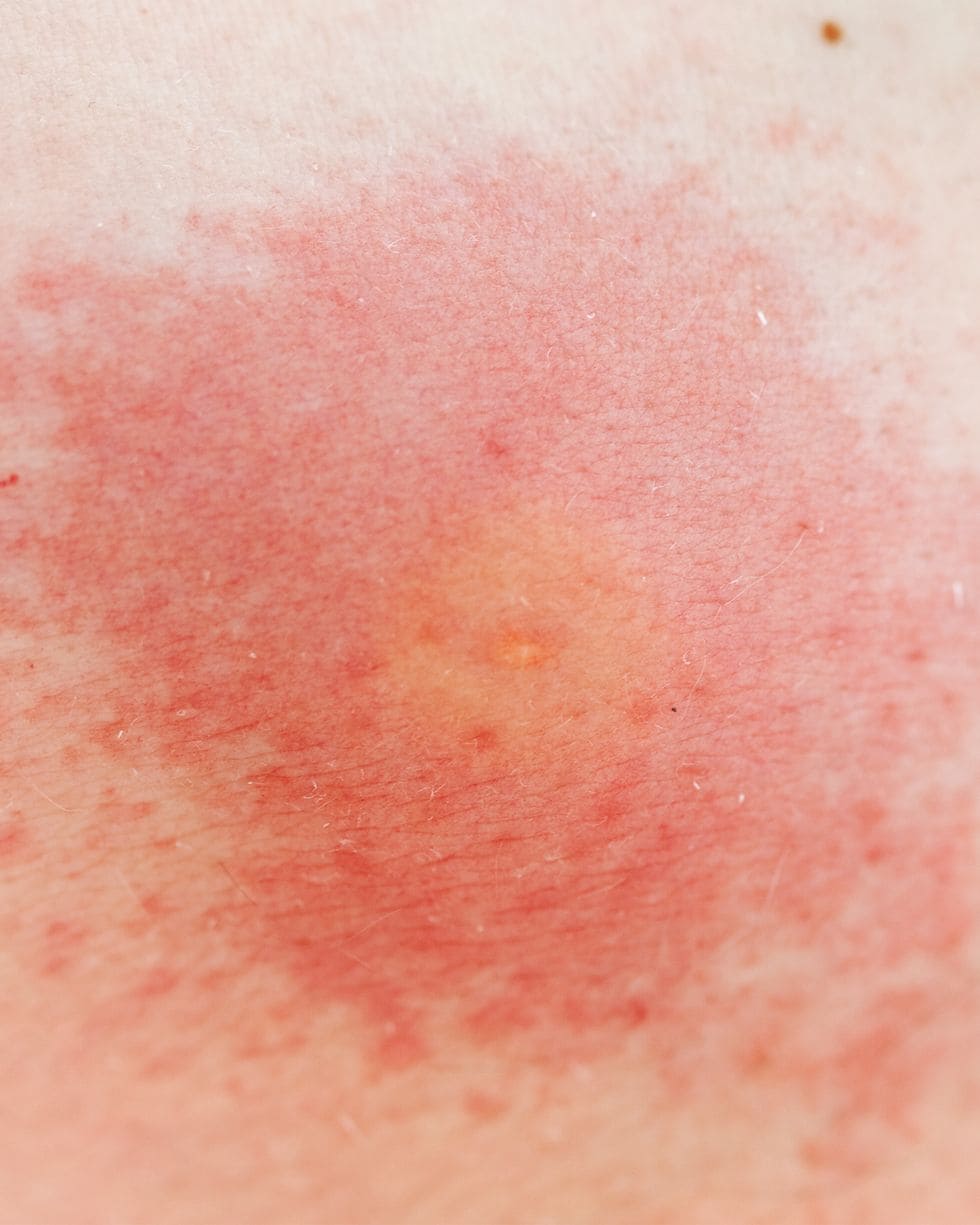
- Ticks can transmit Lyme disease; their bite leaves a rash similar to an expanding bull’s eye.
Most insect bites occur outdoors and are caused directly by the insect. However, there are two exceptions: bedbugs (small mites that live in and around beds) and lice, which are spread through contact with infected people, combs or clothing.
Some insect bites can also transmit diseases, including Zika virus, West Nile virus, Chikungunya virus, and diseases such as dengue fever and yellow fever (all transmitted by mosquitoes), Lyme disease (from ticks), Rocky Mountain spotted fever (from dog or wood ticks), and Chagas disease (from bedbugs).
In a report released in May 2018, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) warned about the increase in recent years of illnesses caused by mosquito, tick and flea bites.
To prevent insect bites, here are some tips from the CDC:
- Use insect repellents registered with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), EEA in Spain (European Environment Agency). The EPA has provided an online tool to help you choose the right one for various conditions.
- When travelling, find out what vaccinations or medications you might need and take precautions.
- Wear clothing that covers the skin when in places with many insects.
Regardless of the type of insect bite, it is helpful to know what stung you. Learning to identify a sting by how it looks and feels will help you decide whether you can treat it at home or need immediate medical attention.
If you have known allergies to insect stings, consult your doctor about emergency care. Some people with severe allergies may require allergy medications, such as epinephrine (like an EpiPen), always on hand.
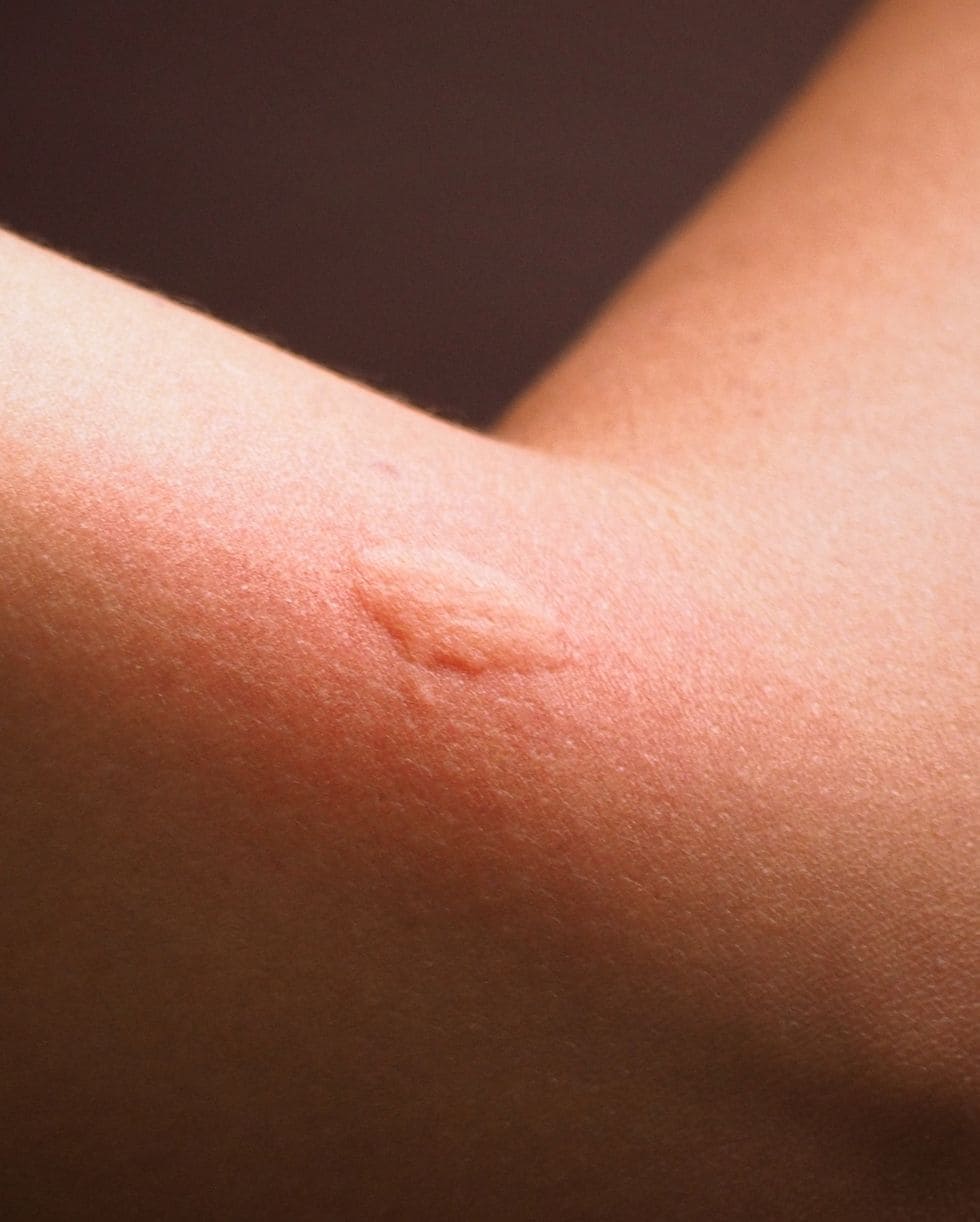
Mosquito Bites and Serious Diseases
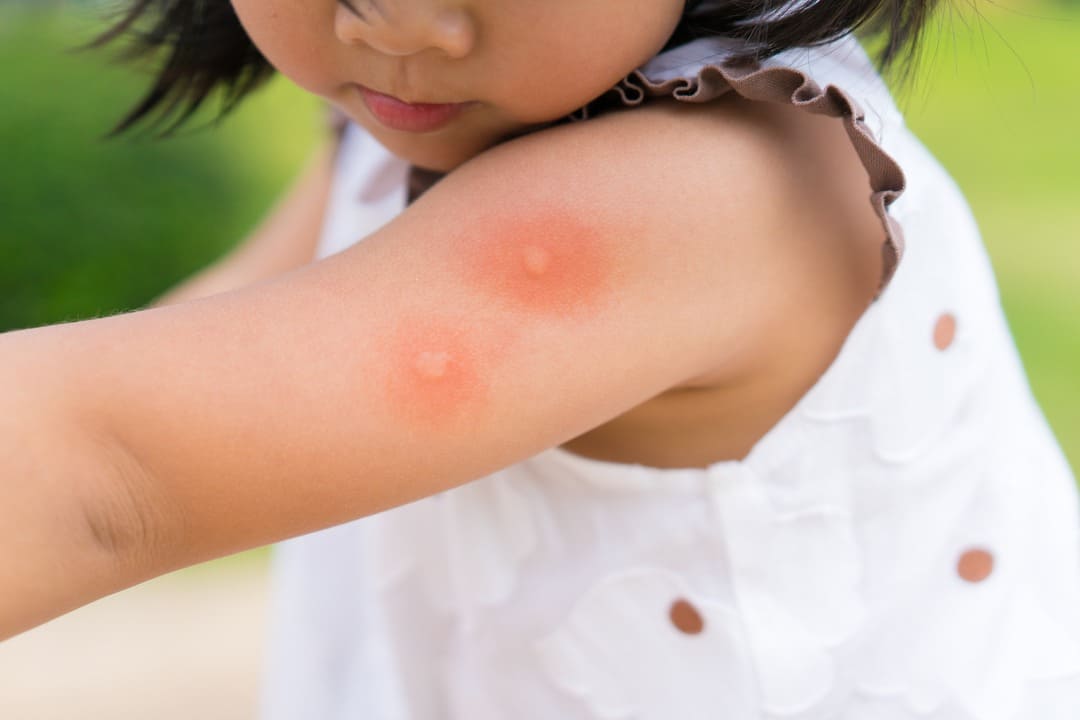

A mosquito bite manifests itself as a round, red or pink, itchy raised bump on the skin. It is usually a harmless bite, but can sometimes lead to serious diseases, such as Zika virus (especially dangerous in pregnant women), West Nile virus, malaria or Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE). While for most, Zika causes a brief flu-like illness, newborns born to infected mothers can suffer from birth defects, mainly microcephaly.
With West Nile virus, symptoms appear 2-14 days after the bite and include headaches, body aches, fever, vomiting, diarrhoea and skin rash. More severe cases may develop into meningitis or encephalitis, characterised by stiff neck, severe headache, disorientation, high fever and convulsions.
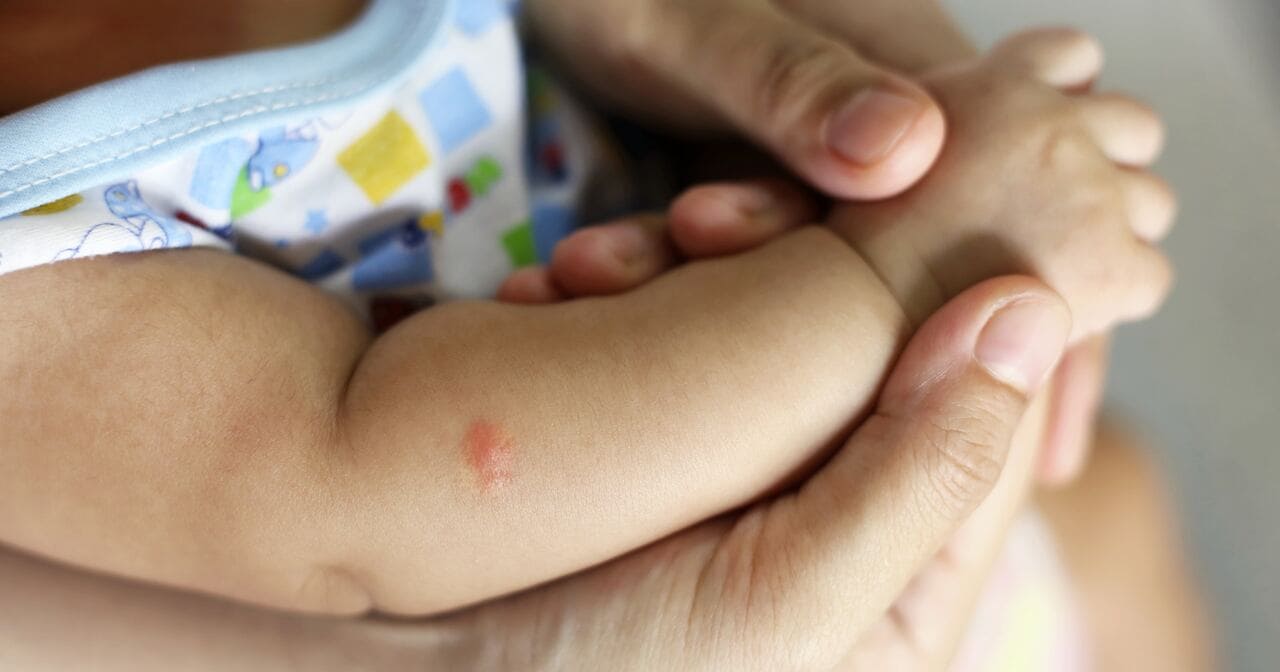

The bite of a parasite-carrying mosquito can cause malaria, a rare condition. Flu-like symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, nausea and vomiting 10 days to four weeks after the bite. Malaria is serious, but it is treatable and preventable.
Cases of EEE are rare but lethal. About 30% of infected people do not survive and many develop neurological problems.
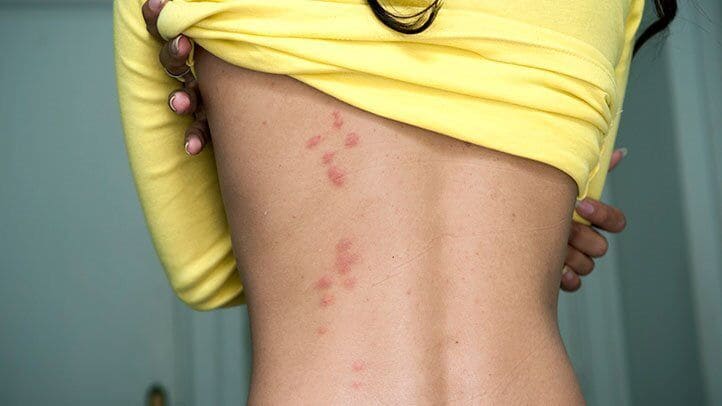
Identifying Bedbug Bites
Although a bedbug bite is usually painless, you may see three or more red marks clustered together, often in a line. In some people, an allergic reaction to the insect’s saliva develops within 24 hours to 3 days, resulting in a red, swollen bump on the skin that itches intensely.
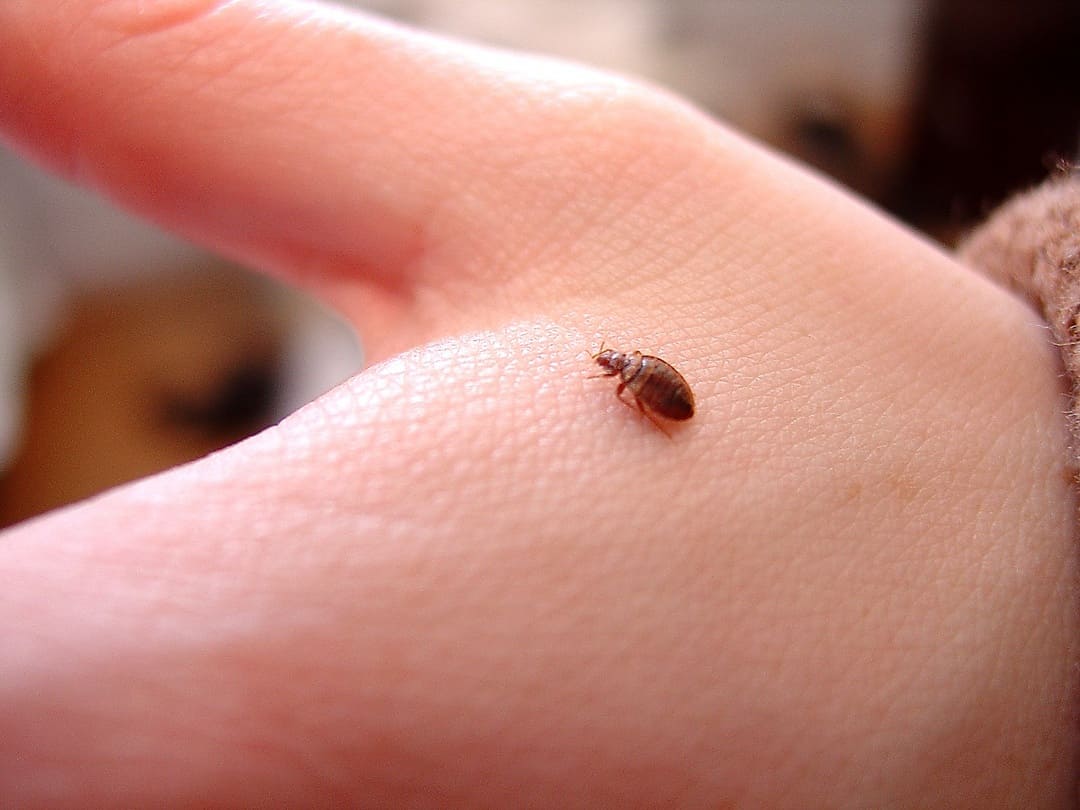

If you develop hives, multiple bites or notice that a bite looks infected, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist for treatment. Bedbug bites can appear anywhere on the body, but are most common on exposed areas such as the neck, face, arms and hands. Although common, bed bugs do not transmit diseases.
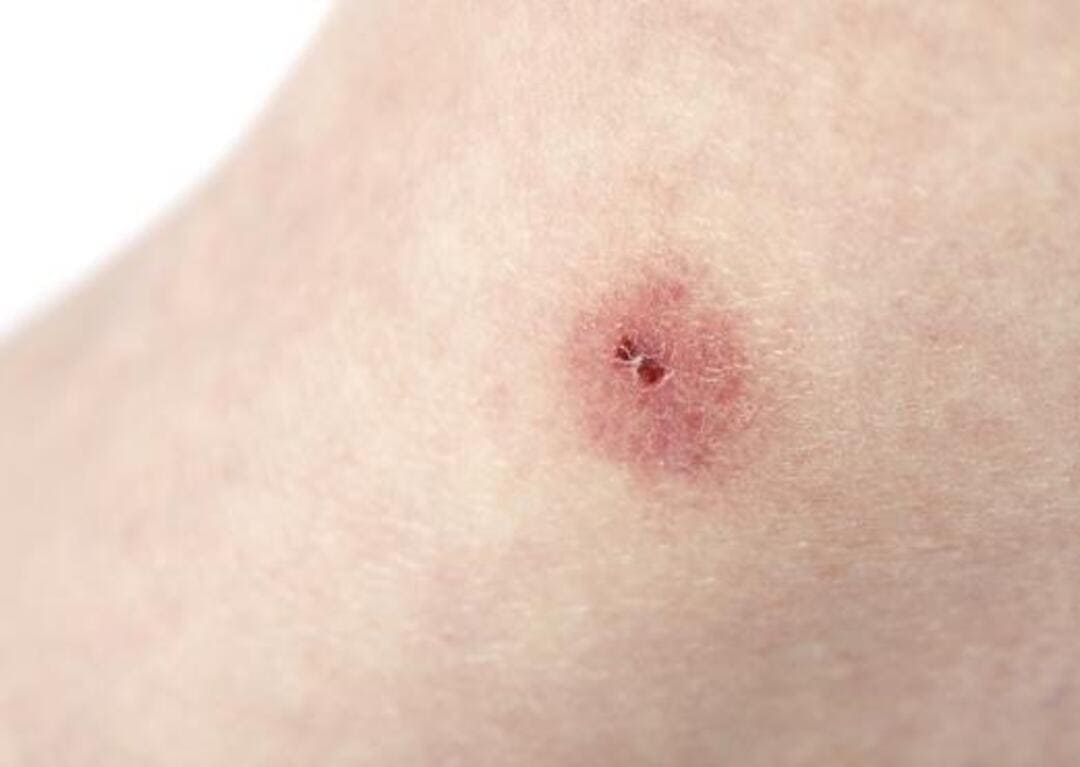
Medical Consultation for Spider Bites
Most spider bites are not poisonous and cause minor symptoms such as redness, swelling and pain in the area. However, some can be a real emergency. If you experience an allergic reaction with symptoms such as chest tightness, difficulty breathing, trouble swallowing or facial swelling, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
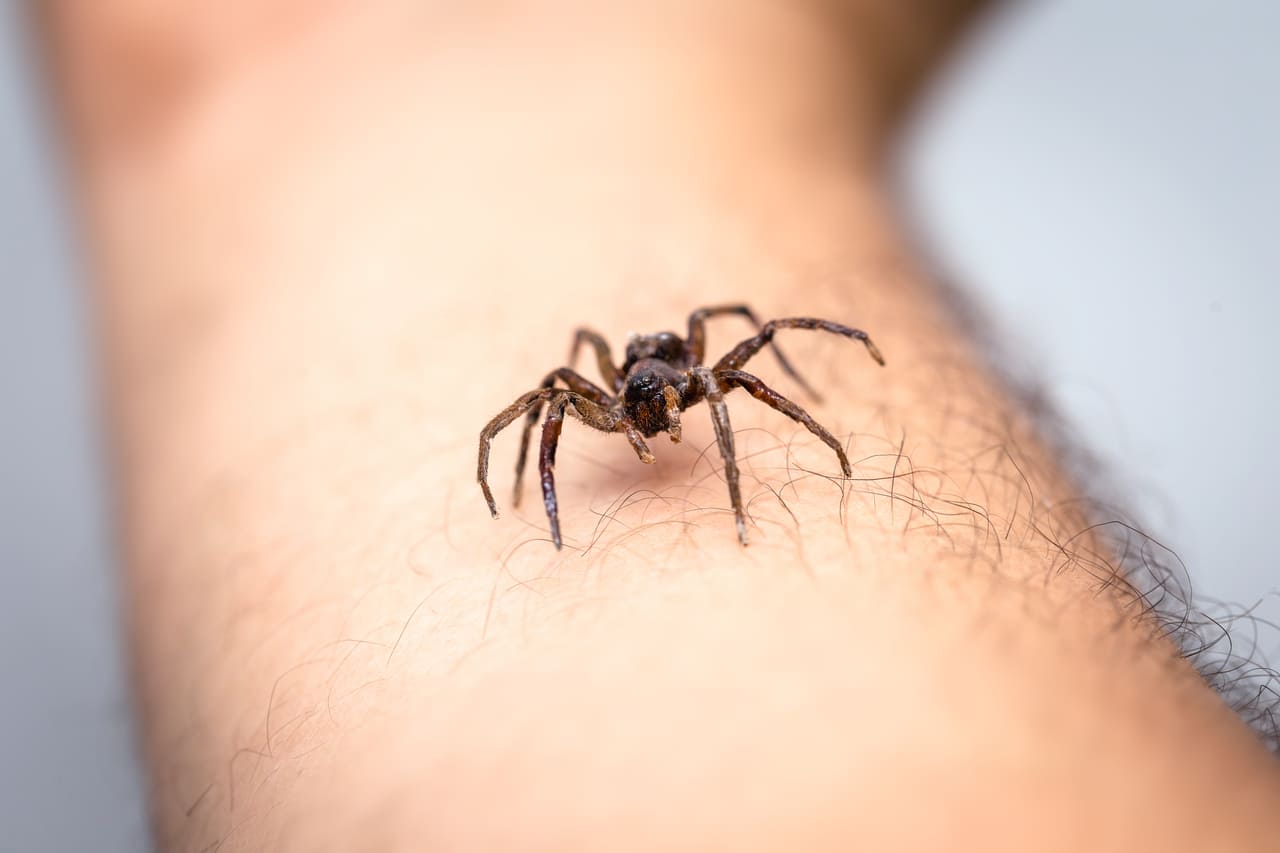

Bites from venomous spiders such as the black widow or brown recluse are extremely dangerous and can cause a severe reaction. The bite of the black widow, which usually has two puncture points, may not be painful at first. However, after 30 to 40 minutes, pain and swelling may appear in the affected area. Within eight hours, muscle pain and stiffness, back and abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and shortness of breath may develop. Even if you did not see the spider that bit you, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention if there is a possibility of a poisonous spider bite.
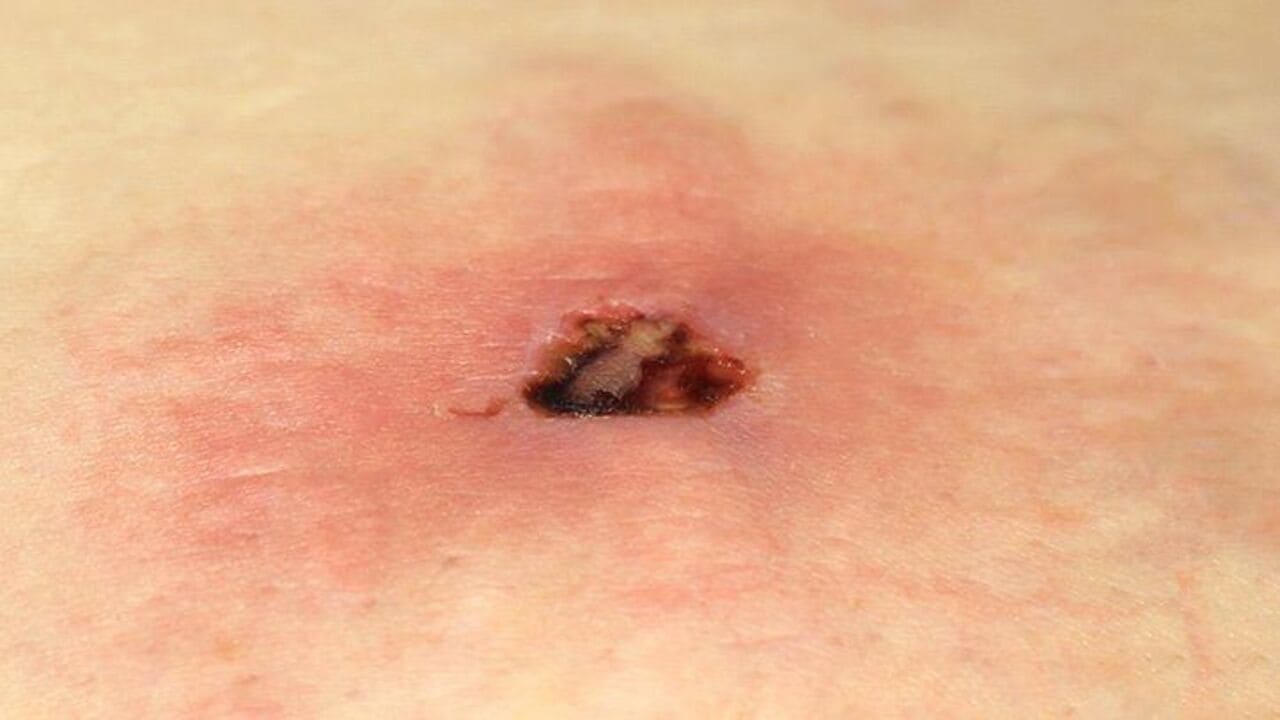
Immediate Care for Brown Recluse Spider Bites
Brown recluse spiders, venomous in nature, tend to inhabit dark, unfrequented places. While some people feel a small prick followed by a sharp pain immediately, others may not notice the bite for several hours. After four to eight hours, the bite may become more painful and appear as a bruise or blister, surrounded by a purplish-blue area. Over time, the bite becomes dry and dark. It should be noted that this type of spider is difficult to find.
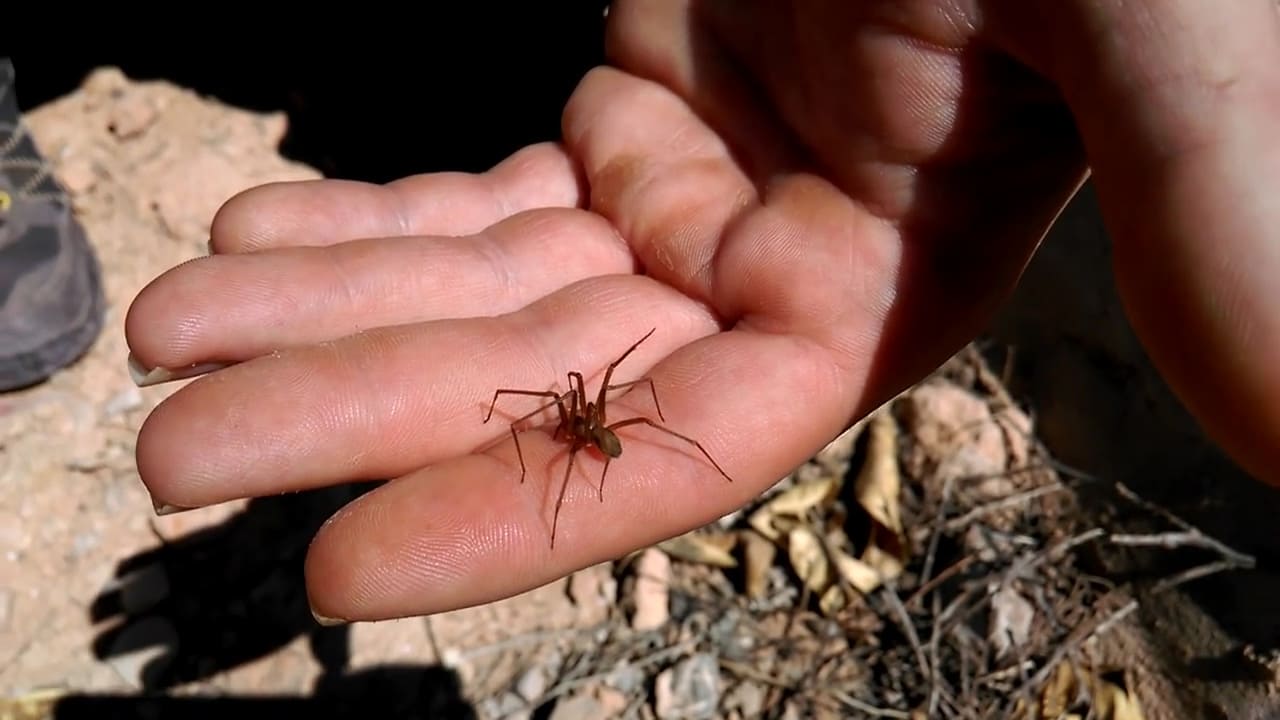

Symptoms of a brown recluse spider bite occur within hours and involve fever, chills, itching, nausea and sweating. Since some people experience a severe reaction that can result in kidney failure, seizures and coma, it is essential to get medical attention immediately. If a poisonous spider bite is suspected, medical attention should be sought promptly.
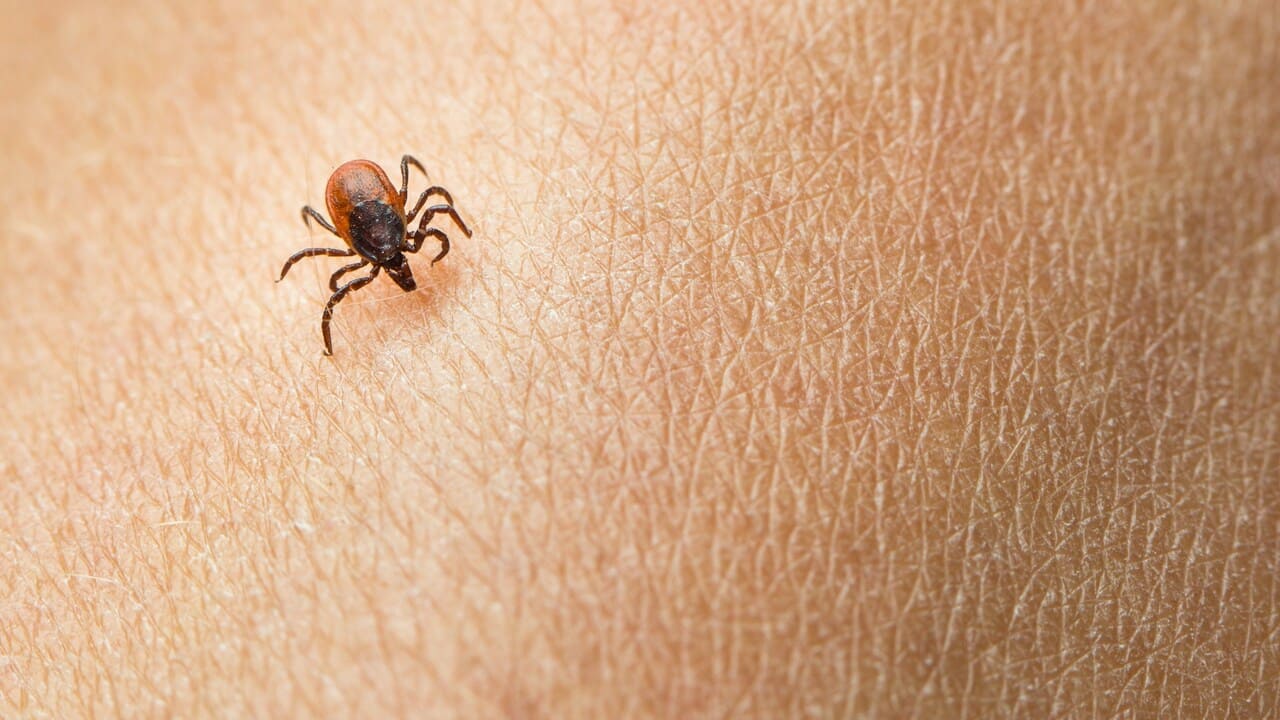

Lyme Disease Transmitted by Certain Ticks
Certain tick bites can be risky because of their ability to transmit disease. Blacklegged ticks, previously known as deer ticks, can carry Lyme disease, while dog ticks can transmit Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Symptoms of Lyme disease include a ring-like rash, resembling a bull’s-eye on a target, which emerges up to a month after the bite. Fever, fatigue, headaches, muscle and joint pain, and irregular heartbeat may also occur. However, 20-30% of infected people do not develop the rash. Advanced Lyme disease can lead to symptoms such as swollen or painful joints, memory loss or autoimmune responses that mimic other diseases. Diagnosis can be challenging because doctors often do not associate these non-specific symptoms with Lyme disease.
Symptoms of Rocky Mountain spotted fever include fever, headache, muscle aches and skin rash. A rash of tiny red spots begins on the ankles and wrists after several days of fever, then spreads to the rest of the body. Some people may not develop the rash. Although this infection can be serious, and even fatal, it can be prevented and effectively treated with immediate medical attention.
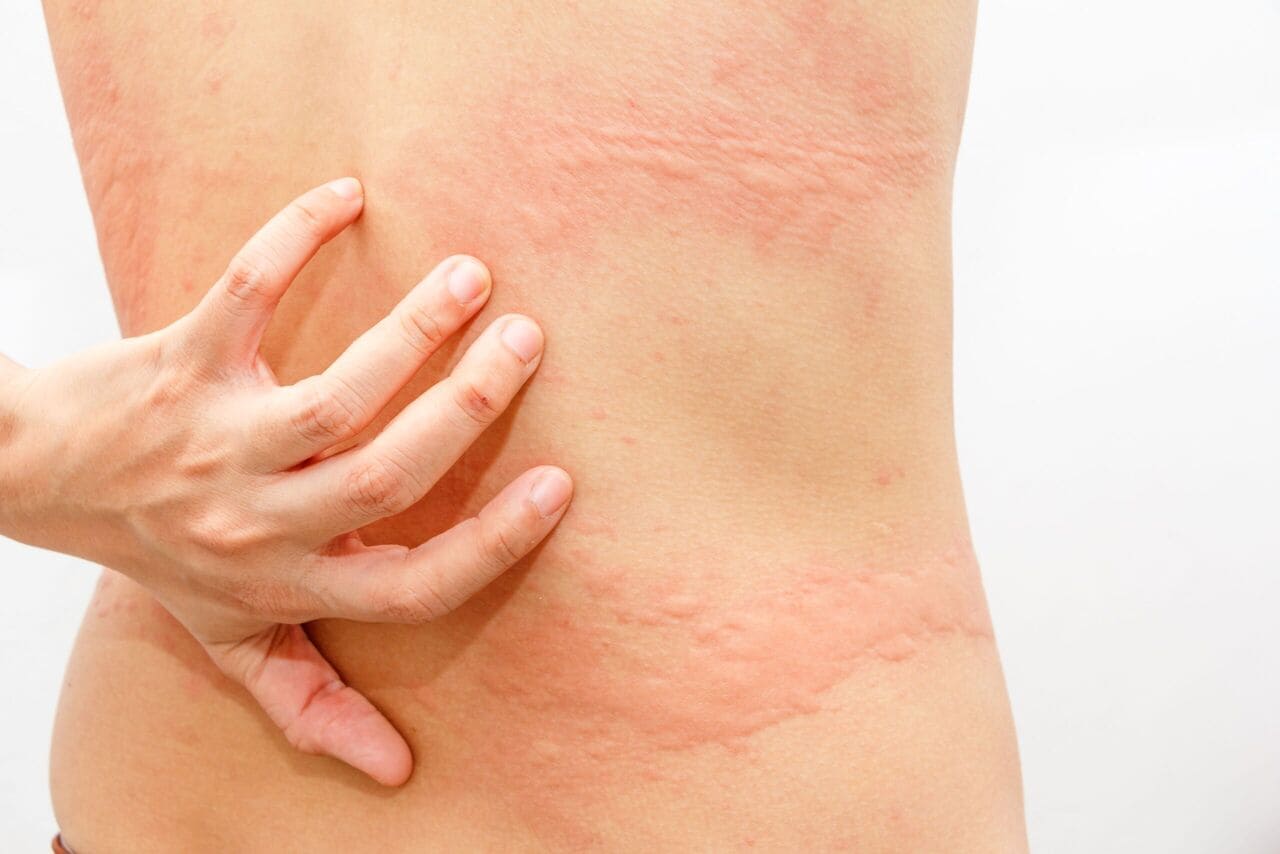
Flea Bite Skin Infections
Symptoms of flea bites can manifest within hours of the bite, and flea bites tend to cluster in groups of three or four. You may notice itching, redness and swelling in the area of the injury or wound, as well as a rash of small red bumps that may or may not bleed. These bites are most common on the ankles and legs, but can also appear in the armpits, around the waist, and on the bends of knees and elbows. A flea bite rash tends to blanch when pressed and tends to increase in size or spread over time. Repeated scratching of the rash can lead to a skin infection, which may require medical attention.
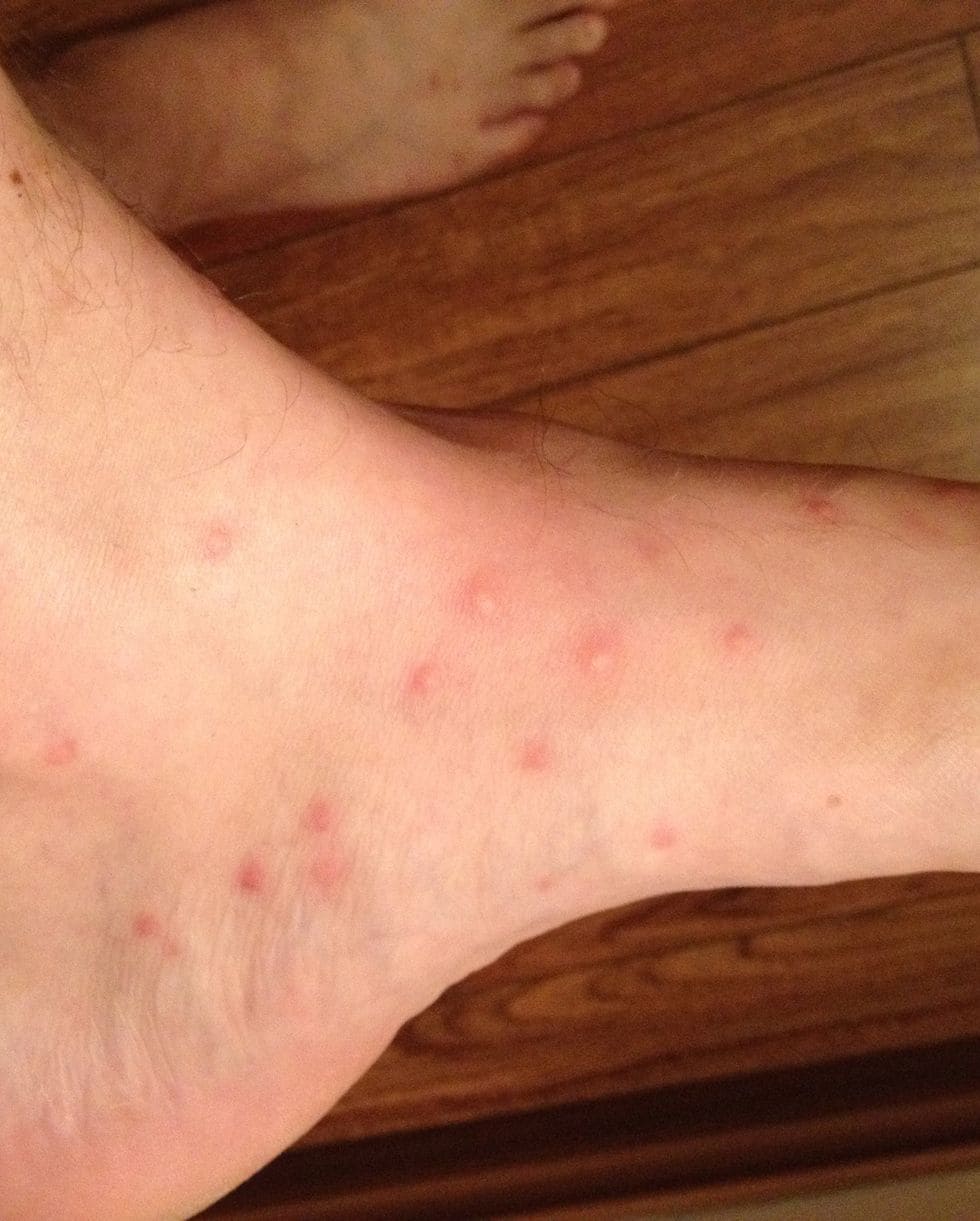
In extremely rare cases, fleas can carry the bacteria that cause plague. The disease can spread from wild rodents to pets and people. Symptoms of plague involve swollen lymph nodes, headache, fever and chills, which occur one to six days after the bite.
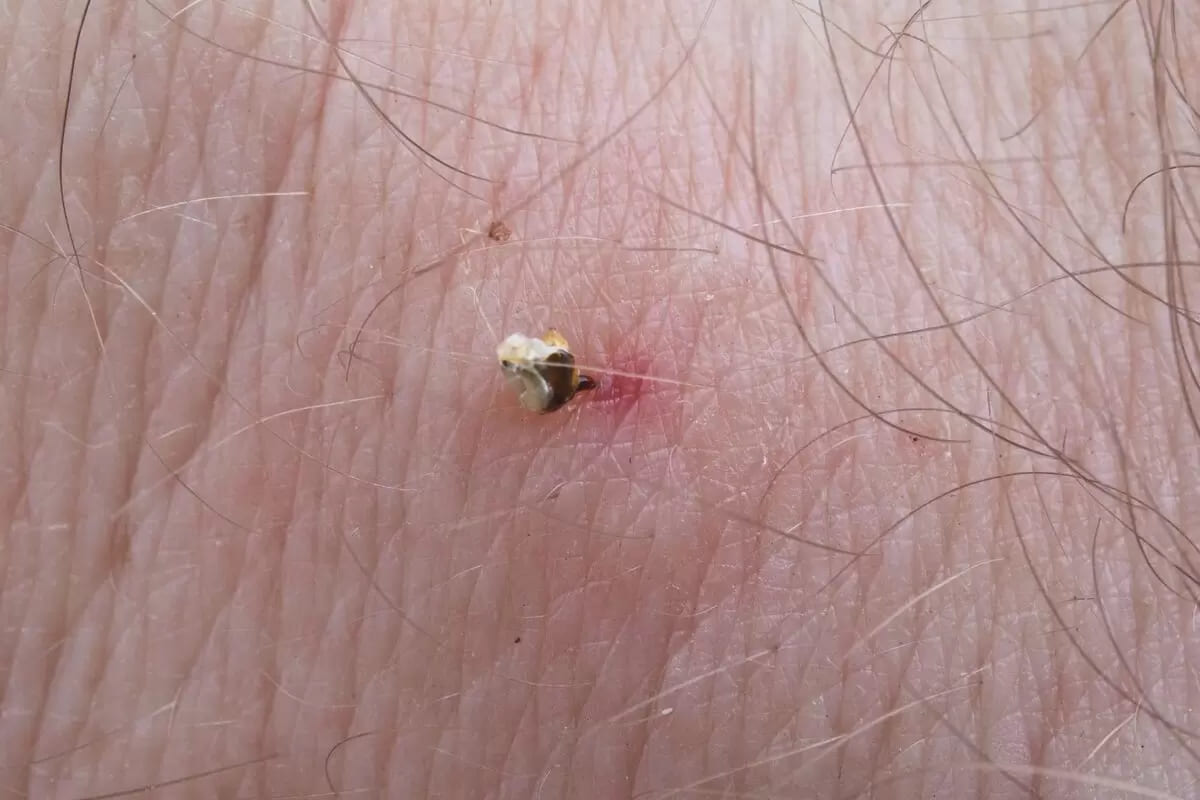
Severe Allergic Responses to Bee Stings
Bee stings cause a sharp painful sensation that may last for a few minutes before progressing to a duller painful sensation. The area may continue to feel sore to the touch for a few days afterwards. Around the site of the bite, a red bump may appear on the skin, surrounded by a white halo. The region may itch and feel warm to the touch.
If you have previously been stung by a bee, your body may react with an immune response to the venom in the sting, causing swelling at the site of the sting or even in larger areas, including the throat and lungs. If you experience this type of allergic reaction, known as anaphylaxis, it is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment. Signs of a severe bee sting allergy include hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, dizziness, cramps, nausea, diarrhoea and even cardiac arrest.
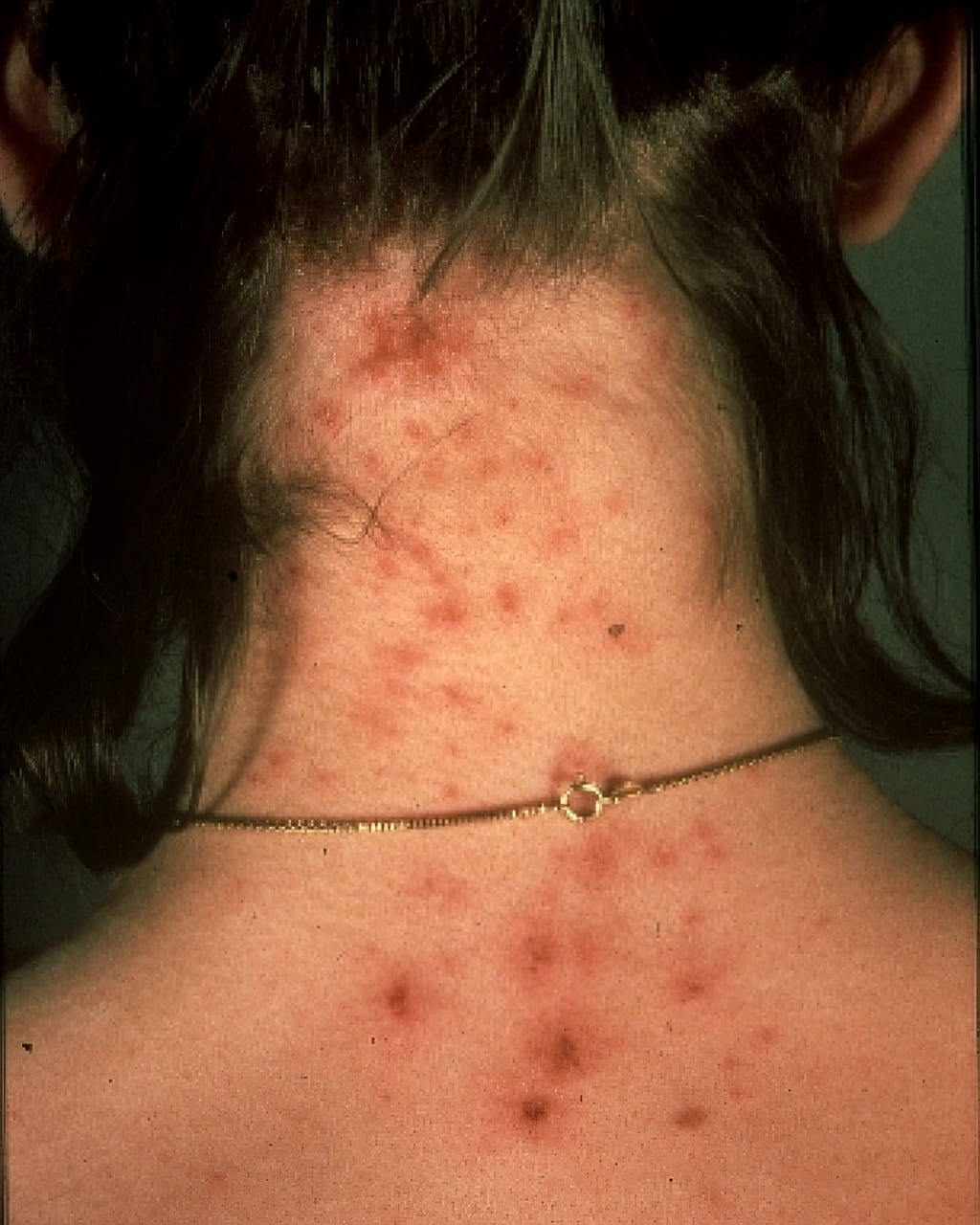
Irritation and Itching from Lice Bites
Lice bites manifest as small red marks on areas such as the shoulders, neck and scalp. These bites are caused by tiny parasitic insects that may inhabit clothing or bedding. Although lice bites are usually small and painless, they can cause an itchy sensation.
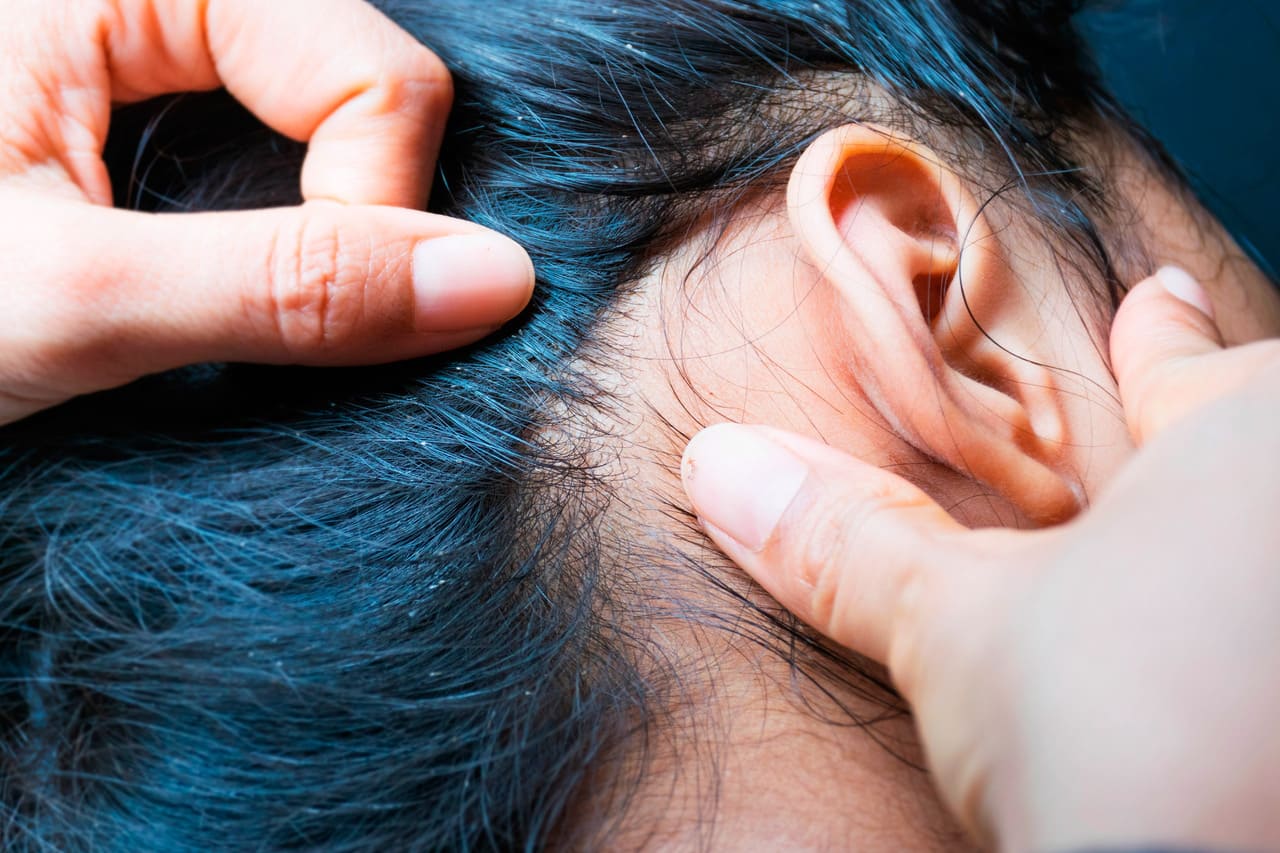
In some cases, people may develop a more extensive and bothersome rash from these bites. Repeated scratching of the affected areas can lead to infections, manifested by symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes and red, tender skin. If a louse bite becomes infected, it may lead to oozing and scabbing; in these cases, medical attention is required, although lice have not been shown to carry other diseases.
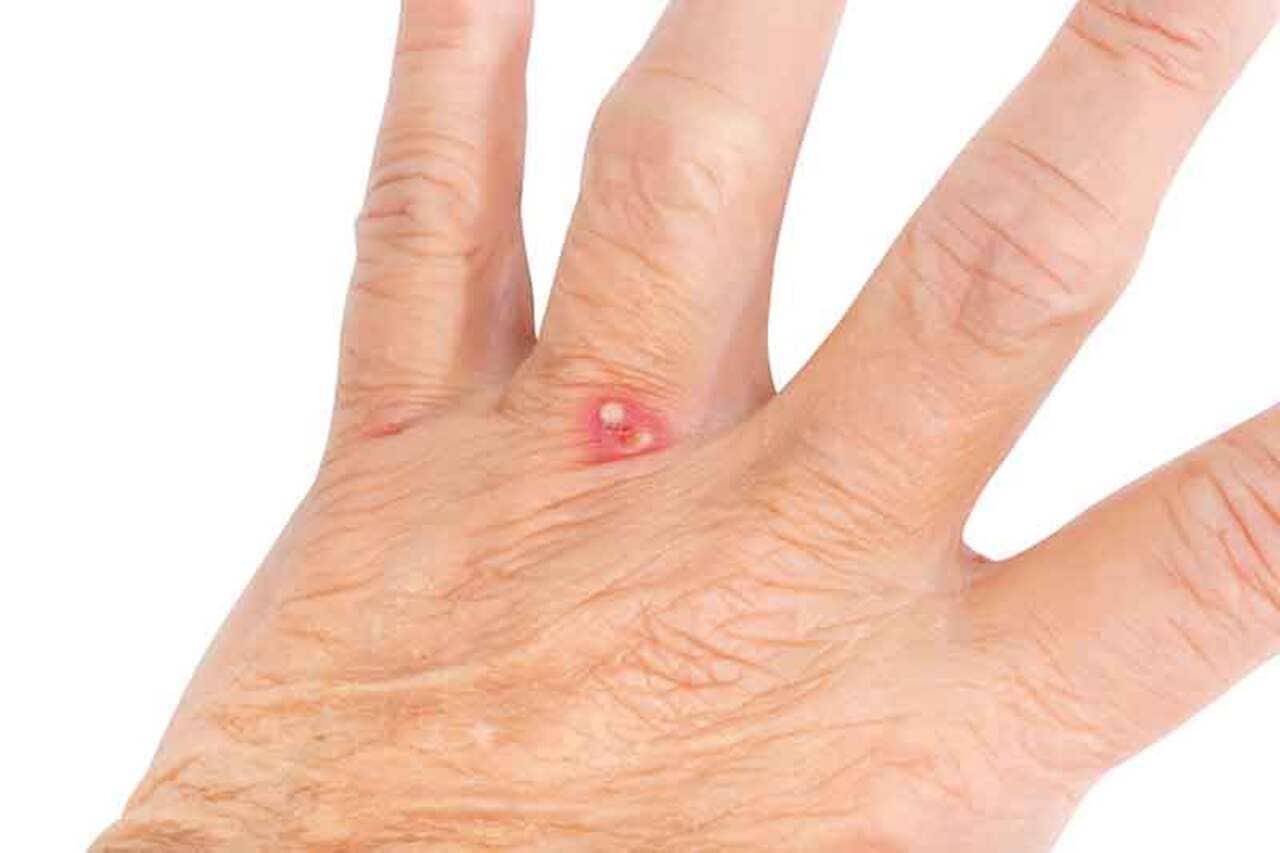
Infections Resulting from Ant Bites
Ant stings, as well as bites, often cause red bumps on the skin and can be painful. Some species, such as fire ants, have venom in their stings that can trigger severe allergic reactions. Fire ants adopt a bite-sting process, which produces a sharp pain and burning sensation. After being bitten by fire ants, it is possible to observe the appearance of white, fluid-filled pustules or blisters within a day or two. These blisters last three to eight days and may leave scars. The bumps may also cause itching, redness and swelling around the site. Caution should be taken not to scratch or open the blisters, as they may become infected. In addition, carpenter ant bites can be painful, as they release formic acid into the bite, which causes a burning sensation.
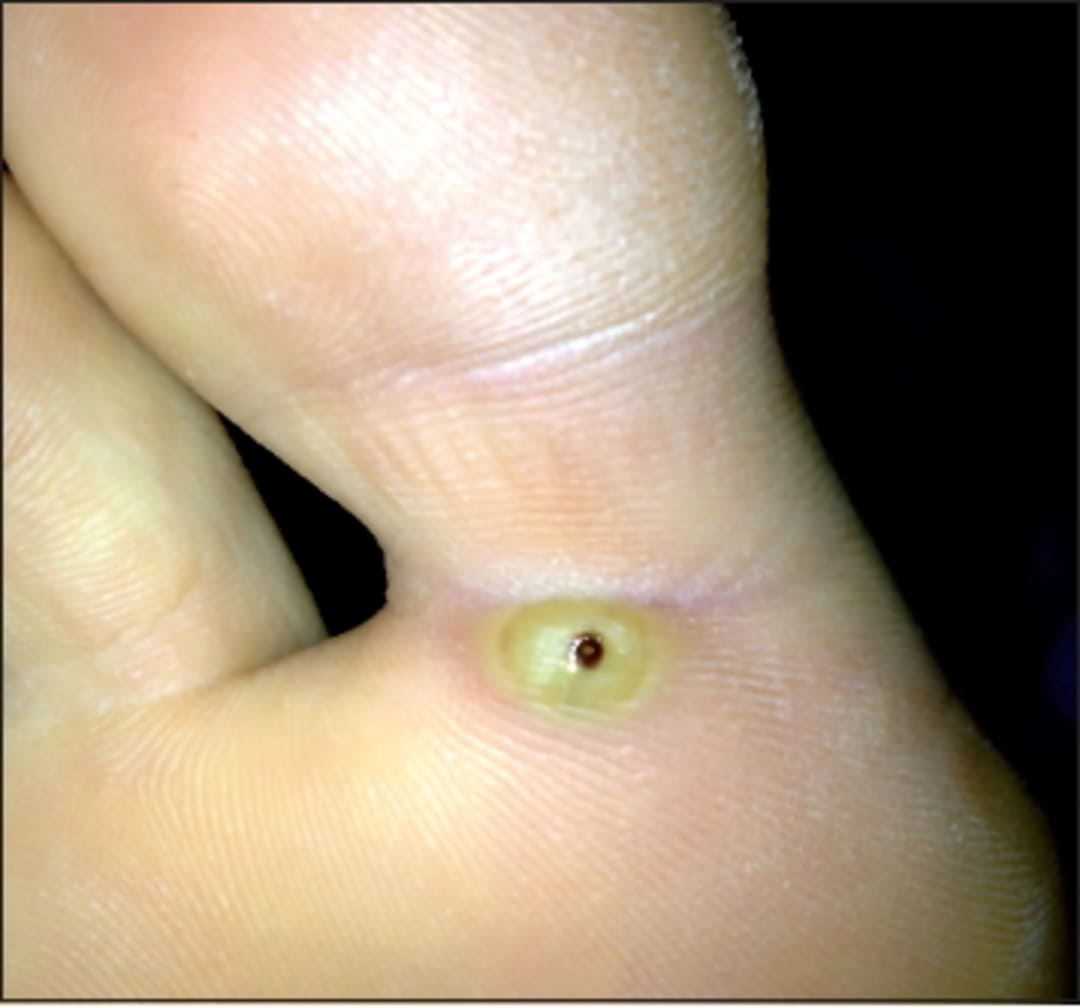
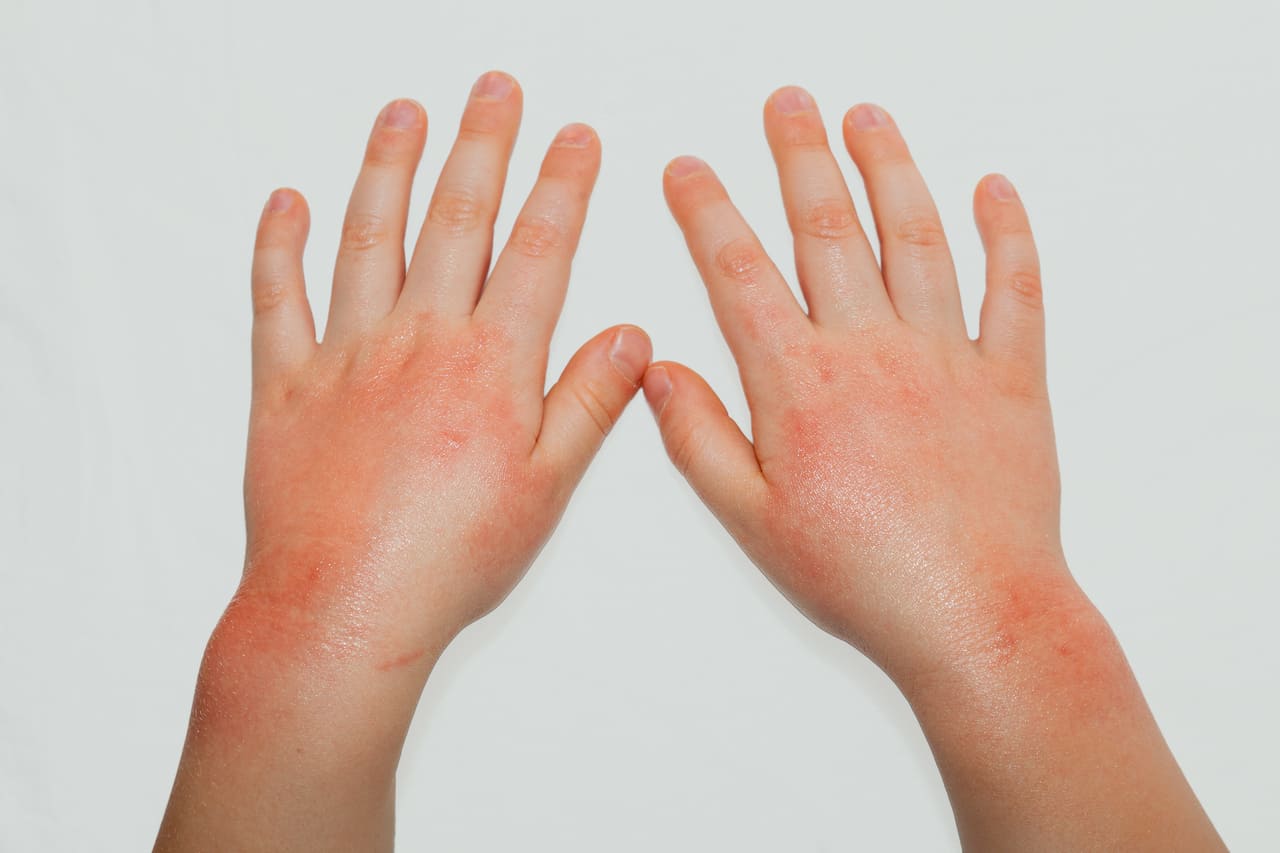
Intense Itching from Mite and Chigger Bites
Although mites generally do not spread disease, their bites can cause irritation and severe itching of the skin. Scabies mites are particularly troublesome, as they cause the disease scabies, which is contagious between people. Female scabies mites burrow into the skin to lay eggs. When the eggs hatch, the larvae emerge on the surface of the skin. They then moult and burrow back into the skin to feed. This leads to the appearance of an acne-like rash and intense itching, which worsens at night.
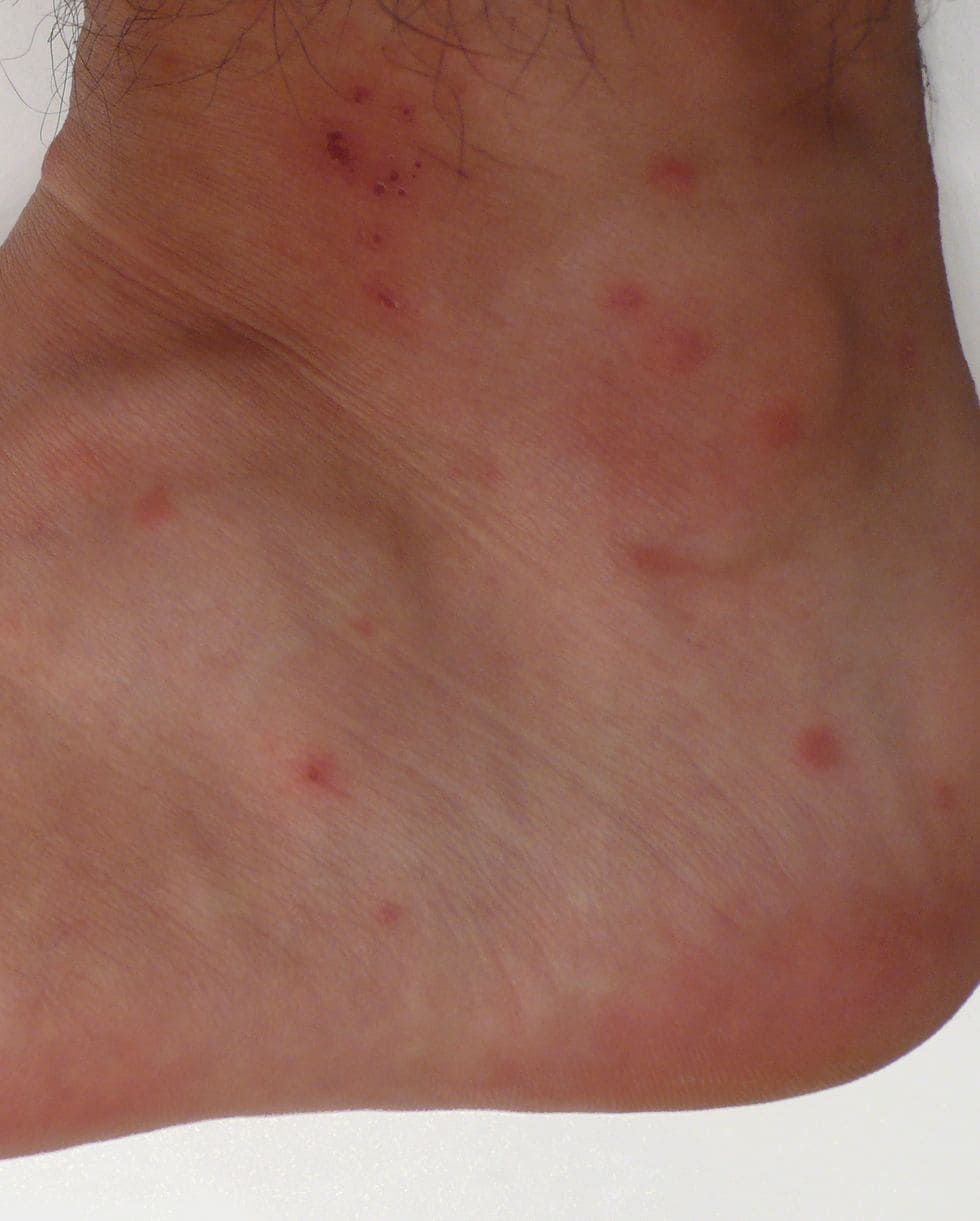
Occasionally, you may notice fine, clear lines on the skin where the mites have burrowed. In addition, chiggers, a form of mite, inject their saliva into the skin to liquefy it and then feed. This causes hardening around the bite, accompanied by irritation and inflammation of the surrounding skin. An itchy, red welt forms in response to the chigger bite.
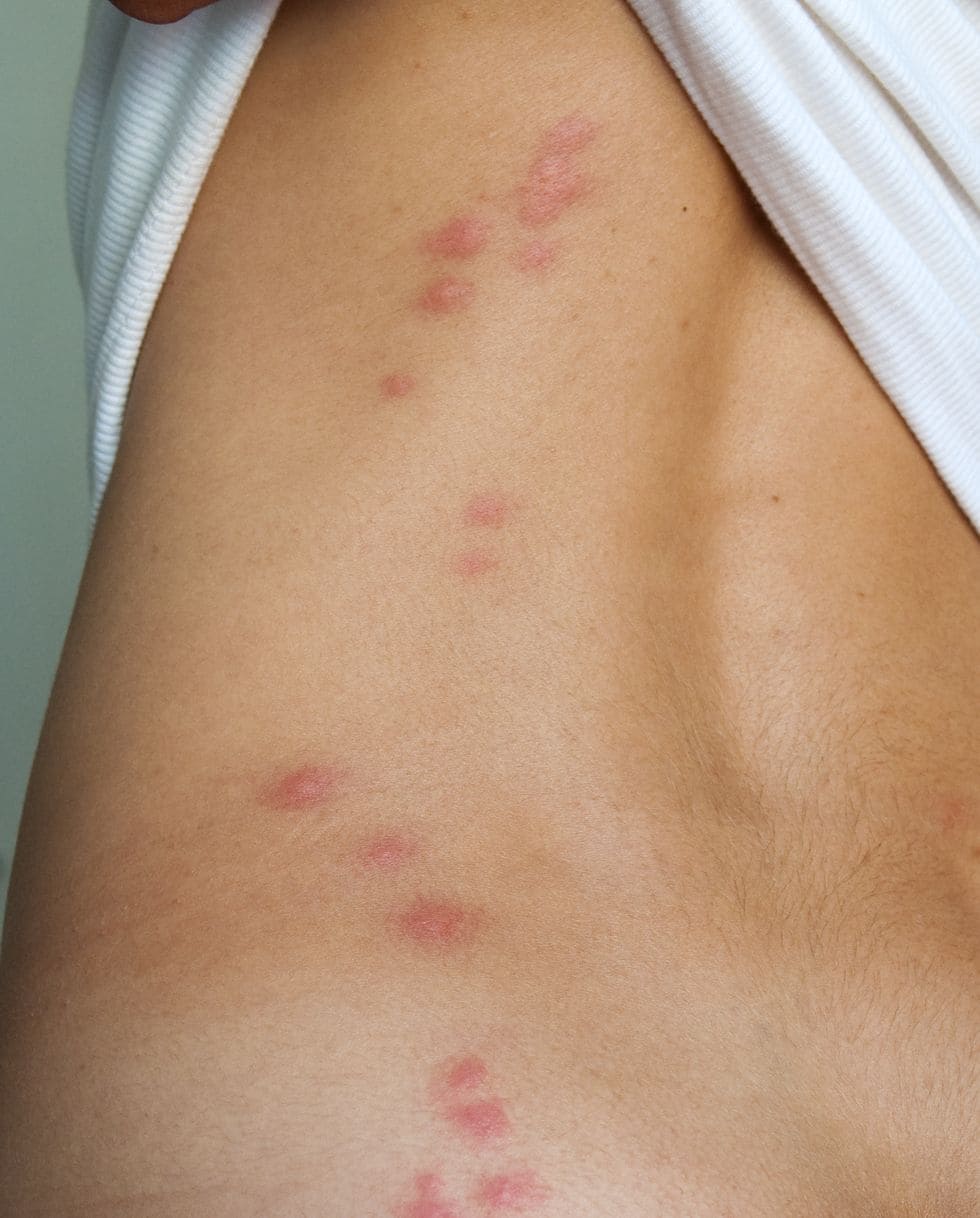
Risk of diseases transmitted by kissing bugs
Kissing bugs, also known as assassin bugs, can transmit parasites that cause Chagas disease. Kissing bugs usually bite at night, leaving bites on the face and causing swelling of the eyelids. In the first few weeks after infection, symptoms of Chagas disease may include fever, fatigue, body aches, headache, rash, loss of appetite, diarrhea and vomiting. In the long term, about 30% of infected persons may develop serious complications, such as enlargement of the heart, heart failure, abnormal heart rhythm, cardiac arrest or enlargement of the colon.
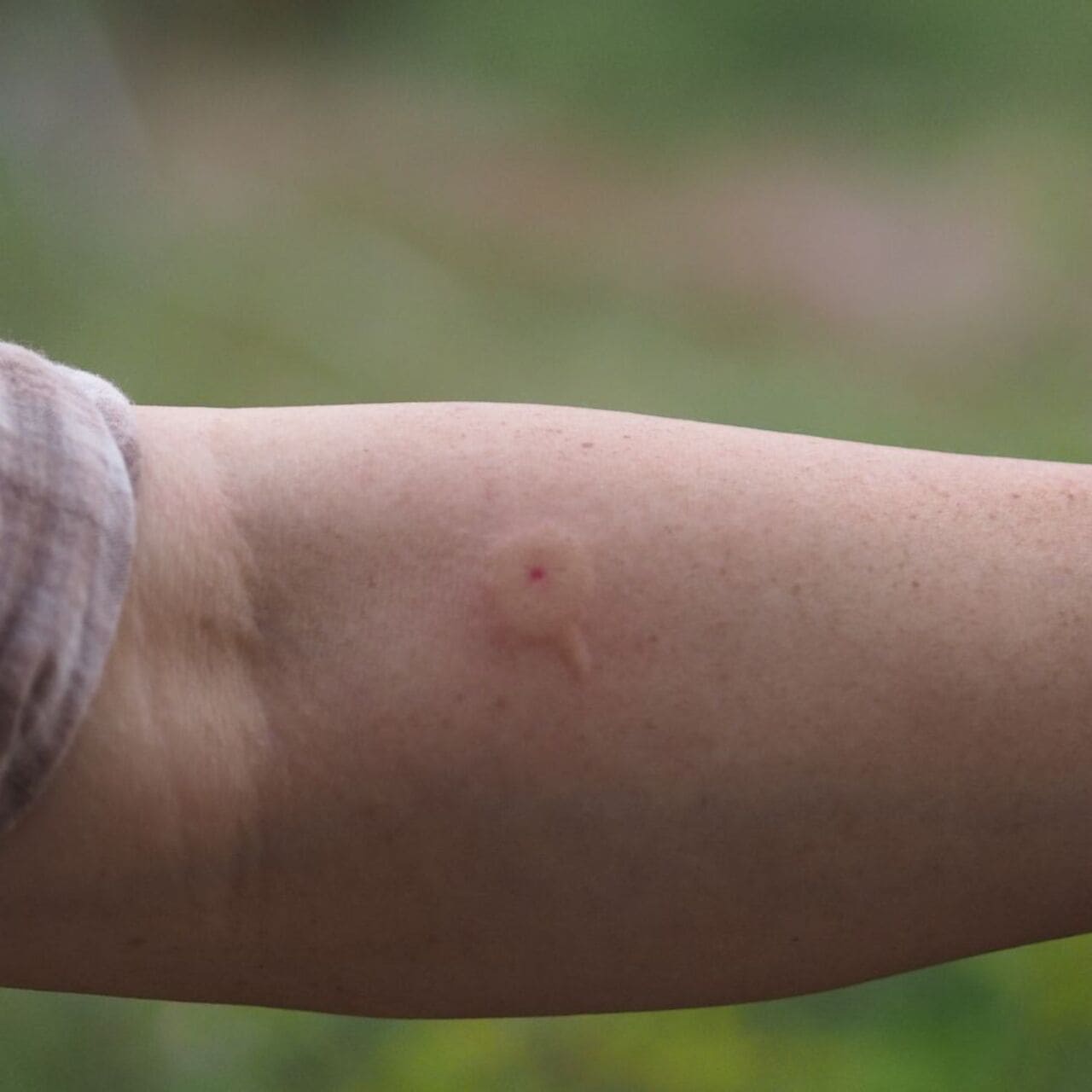
Serious Allergic Reactions to Wasp Stings
Wasp stings (including bee and wasp stings) are often painful and may cause redness and swelling immediately afterwards. However, in most cases, they do not cause lasting effects. People can apply ice to the affected area to relieve pain and take over-the-counter antihistamines to reduce itching. However, for those allergic to bee, wasp or hornet stings, or for those who have been stung repeatedly, a sting can trigger severe allergic reactions, including nausea, palpitations, swelling, dizziness, hives and difficulty breathing. If you experience these symptoms, it is essential to seek emergency medical attention.

Impact of Biting Flies
Although horse flies and deer flies focus more on animals with those names, they can also affect humans. These bites can be painful and cause bleeding, swelling, irritation or allergic reactions. Black flies, also known as “eyeless gnats,” are small and often bite around the head, particularly around the eyes, ears and scalp. Their bites can cause swelling, numbness and pain, which can persist for several days. To prevent these stings, light-colored clothing and insect repellent are recommended.
Treatment of bites
If you have any type of bite similar to all these types of insect bites, please consult your family doctor, in order to receive the best possible treatment.