On this occasion, from Clínica Gran Alacant, we are pleased to discuss what gynecological cytology is for and other aspects related to this common practice.
It is natural that many of our Gran Alacant patients are already familiar with cytology, since it is a fairly routine medical test. For those who have not yet done so, we will now explain what a Pap smear is, what diseases it detects, how a Pap smear is performed, the importance of undergoing this test and the recommended frequency according to age and other relevant factors.
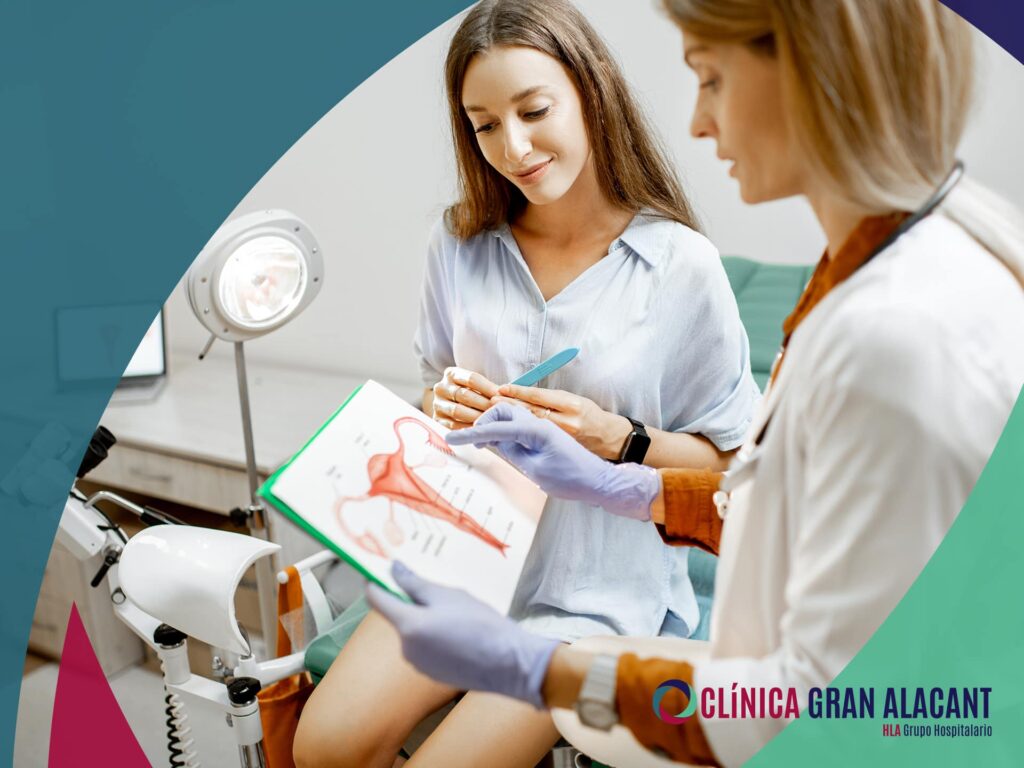
Cytology is a simple gynecological test that facilitates the detection of infections, lesions and even pre-cancerous and cancerous pathologies in the female reproductive system. The word “cyto-” derives from the Greek “cell”, and the test consists of analyzing cells from the vagina and/or cervix under a microscope. Also known as the Pap smear, it is named after the professional who invented it.
Is the gynecological cytology painful?
We can describe the Pap smear as more of an uncomfortable experience than a painful one. A slight pinch may be experienced, but it is of short duration, similar to a small twinge. In rare cases, slight bleeding may occur after the test, which is normal and should not cause concern.
How a Pap smear is performed
The procedure is simple and quick, usually taking no more than five minutes. With the patient lying on her back, the specialist uses a speculum to open the vaginal walls and access the cervix. Then, with a “little brush”, a scraping is performed to obtain the sample. If it is a cervical cytology, tissue is taken from the cervix, and if it is a vaginal cytology, samples are taken from the vaginal walls. The sample is placed in a tube for further analysis in the laboratory.
What is cytology used for?
The main purpose of cytology is to detect cancerous cells, especially in the case of cervical cancer, which tends to be silent and is often detected in advanced stages. Cytology is also effective in identifying the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), responsible for most cases of cervical cancer. In addition, it helps in the diagnosis of vaginal infections caused by bacteria, fungi or sexually transmitted diseases.
How often is a Pap smear done?
The Spanish Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics (SEGO) recommends the first cytology at the age of 25, although some specialists suggest considering it after the first sexual relations or from the age of 20. In sexually active women, it is advisable to perform a gynecological check-up with cytology annually. The frequency may vary according to the age and medical history of each person. Generally, it is advisable to do a cytology test every 3 years, between the ages of 24 and 30, and every 5 years after 30.
What diseases are detected in a cytology
The cytology is presented as an essential test to safeguard women’s health, as it enables the early identification of abnormal cells in the cervix. In case of a positive result, more appropriate treatments can be started earlier.
Specifically, let’s see what diseases are detected in a cytology:
- Cervical cancer: The test is crucial for early detection of cancerous cells in the cervix, allowing for quick and effective interventions.
- Premalignant lesions: In addition to identifying cancer, cytology is effective in detecting precancerous lesions, providing the opportunity to intervene before they evolve.
- Alterations caused by human papilloma virus (HPV): Cytology is essential for the identification of alterations caused by HPV, helping to prevent and treat possible complications.
- Vaginal infections: The test covers the detection of vaginal infections caused by fungi, bacteria and parasites, providing key information for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Vaginal cell disorders due to menopause: Cytology not only focuses on detecting specific conditions, but also addresses vaginal cell-related disorders that may arise during menopause, allowing for comprehensive care of women’s health at different stages of life.
Preparation for cytology and results
Cytology, being a simple test, does not require special preparation. However, it is important to take into account indications before a cytology:
- How long without intercourse: Avoid sexual intercourse 48 hours before the cytology.
- Can you have a pap smear on your period? It is recommended not to perform the cytology during menstruation; it is advisable to schedule it at least 3 or 4 days after the bleeding has ended.
- It is not advisable to perform the cytology if you have recently received treatments with vaginal ova, vaginal creams or spermicides.
Is it normal to bleed after pap smear
During the cytology procedure, which involves inserting a spatula to sweep the circumference of the cervix and a brush into the opening of the cervix, spontaneous bleeding may occur, especially if there is inflammation in the tissue. This bleeding, although it may arise as a natural response to the manipulation of the instruments, carries no special connotation and should not cause concern.
It is important to understand that it is normal to bleed after cytology. Occasional subsequent bleeding is a common phenomenon and is generally considered normal. Inflammation of the cervical tissue may increase susceptibility to bleeding during specimen collection. However, this event should not cause undue concern.
How long does bleeding last after a Pap smear?
It is recommended that you follow the usual protocol, obtaining the cytology results and scheduling a follow-up visit with your health care provider to discuss any findings and receive additional guidance. Most of the time, bleeding associated with cytology is mild, a mere trickle that resolves on its own within a day. However, it is critical to maintain open communication with your gynecologist to address any questions or concerns that may arise.
Cytology test results
When the gynecological cytology yields a negative result, it indicates that the cells are in a healthy state and the results are considered normal. On the other hand, an “inadequate” result suggests that the sample could not be observed correctly, and it is advisable to repeat the test to obtain more accurate results.
In case of abnormalities, the specific findings are as follows:
- ASCUS (Atypical of Undetermined Significance): This result signals that the cells may have abnormalities, although this may be related to infections or even pregnancy. Although it should not cause alarm, this result may require closer follow-up and continued vigilance.
- Low Grade SIL (Low Grade Intraepithelial Lesion): When abnormal cells are found due to Human Papillomavirus (HPV), this result should not generate immediate concern. However, similar to ASCUS, continued surveillance is required to detect possible changes and progression to malignant cells.
- High Grade SIL (High Grade Epithelial Lesion): This result indicates the presence of cells with notable abnormalities and a high probability of progressing to a cancerous state. In general, this result requires an exhaustive study and the implementation of a specific treatment for the patient.
- Carcinoma: When cancerous cells are detected, this result is the most serious and may indicate the presence of cancer. It is essential that, in case of this diagnosis, additional evaluations and tests are performed to determine the extent of the cancer and to plan an appropriate treatment.
How long it takes to get the results of a Pap smear
On average, the results of a cytology test usually take between two and four weeks. In a separate point, obviously related, we discuss the reasons for an altered cytology.
For any other questions, we are in Gran Alacant, to assist you. You can call us at 686 38 92 68, or write to us from our Gynecology web section.